The battery is the key component in the electrification of a stationary or embedded application and allows different energy needs to be met: for example, a computer does not fulfil the same function as an electric vehicle or an energy storage station.
The technology of a battery represents its electrochemical structure. Each technology has its own characteristics in terms of power, the amount of energy stored and the number of charge-discharge cycles.
Therefore, it is very important to choose the battery technology in your solution so that it is the most suitable for your needs.
Battery technology: the 3 most used chemistries
From the development of the first accumulators to the present day, three technologies have been the most used by professionals for the electrification of their solutions. Each of them has different characteristics and is adapted to specific needs.
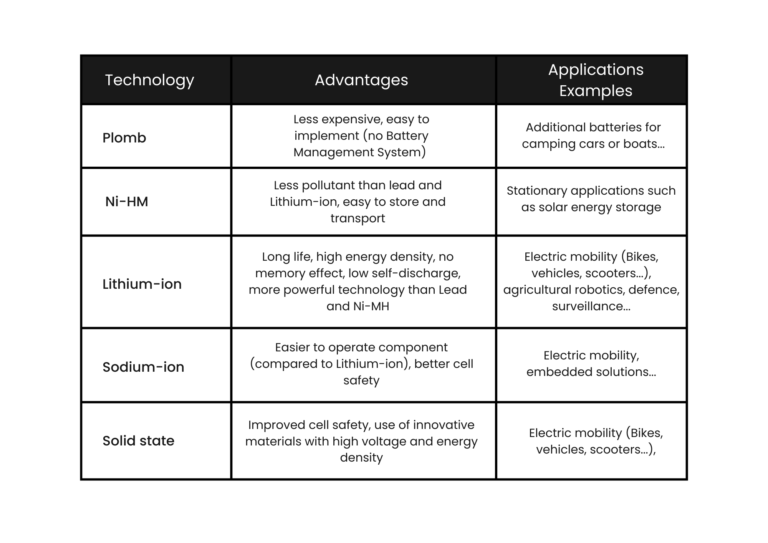
Lead-acid batteries
Invented in 1859, the lead-acid battery is a set of lead-acid accumulators connected in series in the same case. There are also gel batteries, lead-acid batteries in which the acid has been replaced by the gel electrolyte.
Advantages:
- Less expensive than lithium-ion;
- Easy to use (no electronics, especially Battery Management System).
These batteries are mainly used for the storage of electricity and the supply of electrical components in vehicles with internal combustion engines, particularly the electric starter. When the engine is running, it is recharged by a dynamo or alternator.
Nickel Metal Hydride batteries (Ni-MH)
The Ni-MH battery is a rechargeable battery pack that uses metal hydride and nickel. The batteries are based on hydrogen chemistry and redox technology.
Advantages:
- Ni-MH batteries contain more energy than lead or NiCd (Nickel-Cadmium);
- They are less polluting than lead and lithium-ion because they contain only mild toxins;
- They are easy to store and transport because the transport conditions are not subject to regulatory control.
Nowadays, these batteries are most often used as solar batteries for outdoor applications (solar lighting, surveillance, etc.) because of their resistance to extreme temperatures and their safety.
Lithium-ion batteries (Li-ion)
With significant developments in recent years, Lithium-ion batteries are the most widely used for the electrification of various applications, especially in the field of electromobility. Their operation is based on the passage of lithium ions from the anode to the cathode during discharge and the reverse during charge.
Lithium-ion technology includes several chemistries that differ from each other in their characteristics. For example, Lithium Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC) is compact and lightweight with high power for in-vehicle solutions. Lithium Titanate (LTO) has a longer life than most other Lithium sub-categories (between 5000 and 10000 cycles or more).
Advantages:
- Longer life than lead / Ni-Cd / Ni-MH;
- High energy density for a very low weight;
- No memory effect, i.e. a voltage drop that renders the battery unusable when the voltage falls below the minimum threshold for the proper functioning of the device;
- Low self-discharge (<5% per month).
Lithium-ion batteries developed by Neogy® are suitable for several applications such as :
- Electric mobility for electric assisted bicycles;
- Agriculture for agricultural robots;
- Defence for surveillance drones;
- But also aeronautics, aerospace, defence etc.
Battery technology: 2 developments that could revolutionise the current market
Sodium-ion batteries (Na-ion)
Competing with lithium-ion batteries in recent years, sodium-ion batteries technically function like all other batteries. The major difference is that both the cathode and the anode chemistry incorporates sodium.
- Discharge operation: an anode exchanges sodium ions (Na+) for electrons (e-) when the circuit is discharged. The more positive ions (Na+) the battery has to compensate for the negative charge of the electrons (e-), the longer it will be able to supply energy:
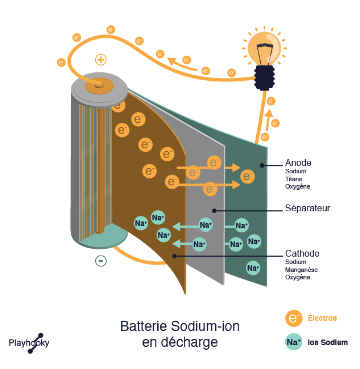
Credits : Playhooky.fr
- Recharge operation: When recharging a Na-ion battery, the electrons (e-) flow in the opposite direction and the sodium ions (Na+) return to their original positions in the anode:
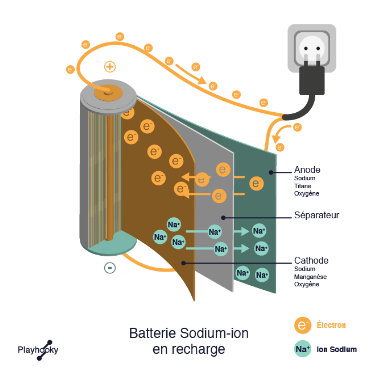
Credits : Playhooky.fr
Sodium-ion batteries are all manufactured for an optimal number of charge-discharge cycles. Today, the power of a Na-ion battery can reach 1 to 5 kW/kg at discharge compared to 0.5 to 1kW/kg for Lithium-ion.
Advantages:
Sodium-ion batteries are not yet able to offer a better energy density than Lithium-ion, especially for electric vehicles, but their use would fill several gaps in Lithium-ion including :
- Scarcity of raw materials: It is possible to find 300 times more Sodium on earth than Lithium. A situation that allows Sodium-ion batteries to be 30 to 50% less expensive than Lithium-ion batteries;
- Battery safety: Na-ion batteries heat up less than Li-ion batteries for example. They are therefore less exposed to the risk of thermal runaway.
Neogy® has been monitoring this electrochemical technology and in order to enable its customers to benefit from its performance, Neogy® has partnered with Tiamat, a French manufacturer of sodium-ion cells, for the design of its battery packs.
Solid state batteries
Solid state batteries represent a real technological evolution compared to the operation of current lithium-ion batteries. In lithium-ion batteries, the ions move from one electrode to another thanks to the liquid electrocyte. In an all-solid battery, the liquid electrolyte is replaced by a solid element that allows the diffusion of Lithium ions.
This concept, which has been in existence for several years, has recently undergone a significant evolution with the arrival of new families of solid electrocytes with a powerful ionic conductivity similar to that of liquid electrolytes.
Advantages:
- Better cell and battery safety: solid electrolytes, unlike liquids, are not flammable when subjected to high heat. All-solid batteries therefore have enhanced safety with better thermal management;
- An innovation in battery design: All-solid batteries allow the use of innovative materials with high voltage and high energy capacity. This makes it possible to design denser, lighter batteries with an optimised life span, ideal for use in electric vehicles, for example.
All these technologies and their developments are driving constant innovation in the battery sector. New technologies are still being tested and will be added to those already in use in order to offer the best performance to professionals and their users.
At Neogy®, each battery pack is tailor-made according to the customer’s needs, an expertise made possible by the diversity of skills within its research and development centre. The electrochemical technology is selected to meet the performance requirements of professionals, particularly in terms of the power, safety, life span and energy density of their battery pack.
Find out how our battery packs can be fitted to your solution.